Privacy and security are often treated as opposing forces in blockchain design. Public networks favor transparency at the cost of confidentiality, while private systems achieve secrecy by reintroducing trust. Dusk Network approaches this problem from a different angle. Instead of choosing one side, it treats privacy and security as co-dependent properties that must coexist—especially in regulated financial environments.
Founded in 2018, Dusk is a Layer 1 blockchain designed specifically for regulated, privacy-focused financial infrastructure. Its architecture reflects a careful balance: transactions must protect sensitive information, yet remain verifiable, auditable, and legally compliant. Understanding how Dusk achieves this requires looking beyond surface-level encryption and into how privacy is embedded into execution, validation, and settlement.
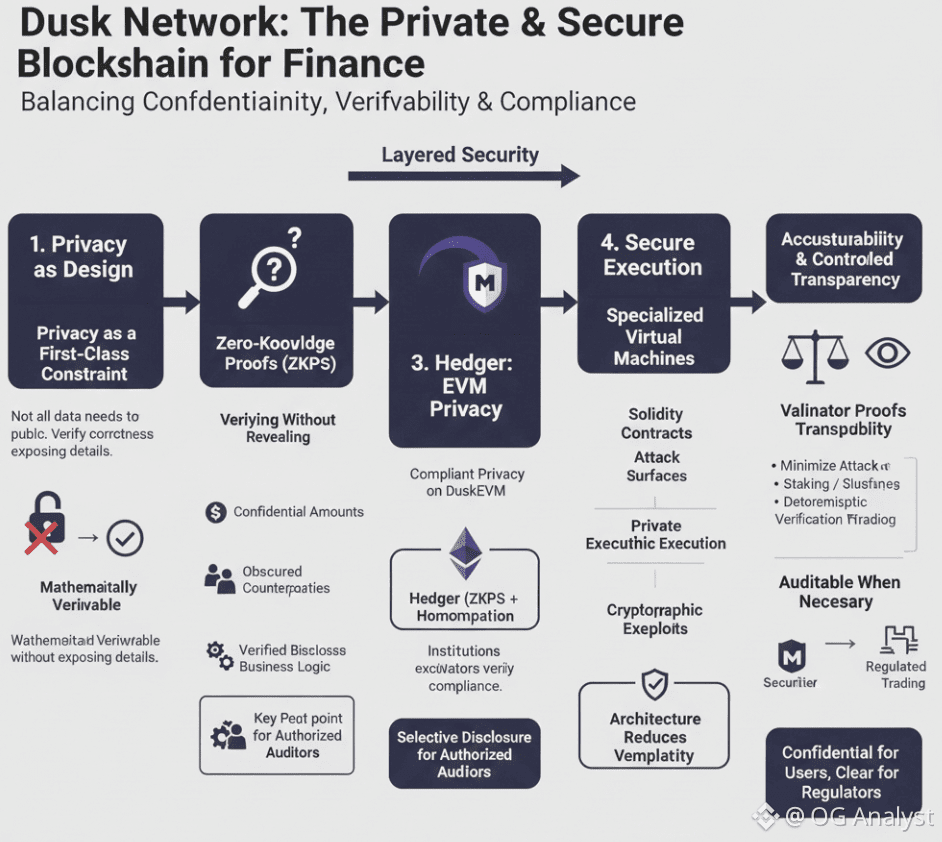
Privacy as a First-Class Design Constraint
In most blockchains, privacy is layered on after the fact—through mixers, add-ons, or optional shields. Dusk takes the opposite approach. Privacy is built into the protocol’s execution model itself.
At the core of this approach is the idea that not all data needs to be public to be trustworthy. What matters is that the network can mathematically verify correctness without exposing sensitive details. This principle guides Dusk’s transaction design, smart contract execution, and validator responsibilities.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Verifying Without Revealing
Dusk relies heavily on zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) to ensure transactional privacy. These proofs allow one party to demonstrate that a transaction is valid—meeting all protocol rules—without revealing the underlying data.
In practical terms, this means:
Transaction amounts can remain confidential
Counterparties can be obscured when required
Business logic can be verified without exposing internal state
Crucially, Dusk’s use of ZKPs is not aimed at full anonymity. Instead, it supports selective disclosure, enabling authorized auditors or regulators to access specific information when legally required.
Hedger: Privacy on EVM Without Breaking Compliance
With the introduction of DuskEVM, Dusk extends privacy guarantees into the EVM environment using a system called Hedger. Hedger combines zero-knowledge proofs with homomorphic encryption to enable privacy-preserving smart contract execution while maintaining auditability.
This is particularly important for financial use cases:
Institutions can execute Solidity contracts without exposing proprietary data
Transactions remain provably correct to the network
Regulators can verify compliance without relying on blind trust
By embedding these capabilities at the protocol level, Dusk avoids the fragility of off-chain privacy solutions.
Secure Execution Through Specialized Virtual Machines
Security in Dusk is reinforced through its modular execution environment. DuskVM and its custom components—such as Piecrust—are designed to handle confidential state transitions safely.
Rather than reusing a general-purpose virtual machine, Dusk built its execution layer to:
Minimize attack surfaces for private computation
Ensure deterministic execution for verifiable proofs
Align execution costs with cryptographic complexity
This specialization reduces ambiguity in smart contract behavior, which is a frequent source of exploits in more generalized environments.
Validator Accountability and Cryptographic Guarantees
Privacy does not eliminate the need for strong economic security. Validators in the Dusk Network stake the native Dusk token and are economically accountable for correct behavior.
Security is enforced through:
Slashing conditions for protocol violations
Cryptographic verification of execution results
Transparent consensus rules that are independent of private transaction data
Validators never need to see sensitive transaction details, yet they can still verify validity. This separation of knowledge and verification is a cornerstone of Dusk’s security model.
Auditability Without Surveillance
A key challenge for privacy-focused systems is auditability. Dusk addresses this by enabling controlled transparency. Transactions can be inspected by authorized parties without making the entire ledger public.
This is particularly relevant for:
Tokenized securities
Regulated trading platforms like DuskTrade
Institutional reporting requirements
Instead of exposing everything to everyone, Dusk allows access to be cryptographically gated, ensuring privacy for users and clarity for regulators.
A Different Security Philosophy
Dusk’s approach reflects a broader shift in blockchain thinking. Security is not just about resisting attacks; it is about maintaining trust in environments where legal, financial, and technical requirements overlap.
By integrating privacy-preserving cryptography, secure execution environments, and accountable validators, Dusk creates a system where transactions are:
Confidential by default
Verifiable by design
Auditable when necessary
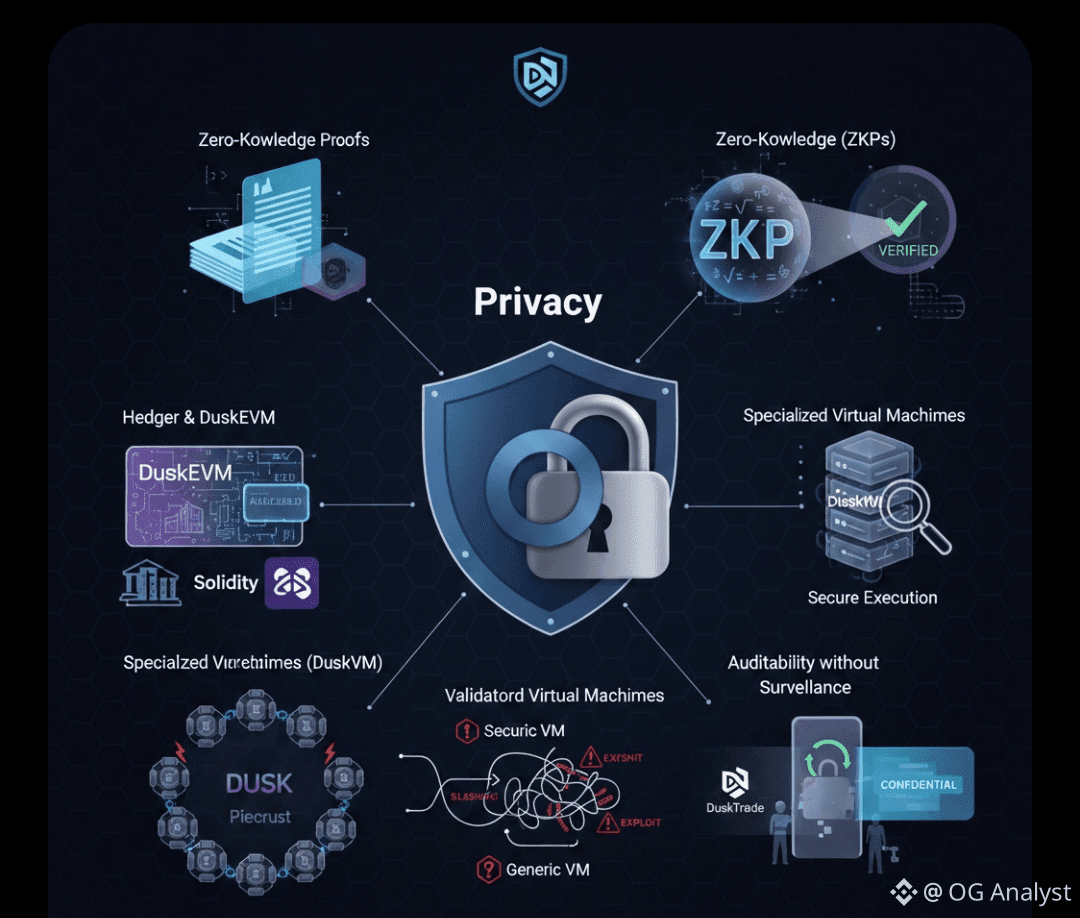
Conclusion
Dusk Network ensures privacy and security not by obscuring activity, but by redefining how trust is established. Through zero-knowledge proofs, compliant privacy tools like Hedger, specialized virtual machines, and economically aligned validators, Dusk enables transactions that are both confidential and credible.
In a blockchain industry often split between radical transparency and closed systems, Dusk demonstrates that privacy and security do not have to compete. When designed carefully, they reinforce each other—and make regulated, real-world finance on-chain genuinely viable.


