
5,584 transactions per second. That's what Kaspa achieved during its October 2025 mainnet stress test , that's roughly 20x Visa's average throughput and 833x faster than Bitcoin, and all while maintaining Bitcoin-level security through proof-of-work consensus.
Kaspa is a Layer-1 proof-of-work blockchain that solves the fundamental speed-security tradeoff that has plagued cryptocurrencies since Bitcoin's inception. Instead of forcing miners to compete in a zero-sum race where only one block wins, Kaspa's blockDAG architecture allows all honest blocks to be included simultaneously, creating a parallel processing system that scales throughput without sacrificing decentralization.
At its core, Kaspa addresses what many consider the blockchain trilemma's most stubborn constraint: the assumption that consensus must be linear. By implementing the GHOSTDAG protocol, a mathematical breakthrough that extends Nakamoto consensus to directed acyclic graphs, Kaspa achieves 10 blocks per second with sub-second confirmation times while maintaining the security guarantees that make Bitcoin the most trusted digital asset. With 598.82 PH/s of hashrate securing the network and a completely fair launch (zero premine, zero VC allocation), Kaspa represents the most serious attempt to scale proof-of-work without compromising its foundational principles.
▨ The Problem: What's Broken?
🔹 Speed-Security Tradeoff Assumed Inevitable → Bitcoin processes 0.17 blocks per second with 10-minute confirmation times, while faster chains sacrifice security through weaker consensus mechanisms or proof-of-stake validators that can be slashed or corrupted.
🔹 Mining Centralization Through Block Competition → In traditional blockchains, only one miner wins per round, creating variance that drives smaller miners toward pools. This zero-sum competition concentrates hashpower in the hands of a few large operators.
🔹 Orphaned Work Wastes Energy and Security → When multiple miners find valid blocks simultaneously, all but one are discarded as "orphans," wasting computational work and the security that work represents. This fundamental inefficiency limits how fast blocks can be produced.
🔹 Linear Consensus Creates Artificial Bottlenecks → Existing blockchains force transactions into single-file processing, ignoring the parallel nature of modern computing. This creates artificial scarcity in block space and drives up fees during network congestion, as seen in Bitcoin's $7+ fee spikes during high usage periods.
▨ What Kaspa Is Doing Differently
Kaspa breaks the linear consensus assumption by implementing a blockDAG (directed acyclic graph) where miners simultaneously create blocks that reference all previous "tips" they observe, forming a web of interconnected blocks rather than a single chain. This architectural shift enables what traditional blockchain design considered impossible: accepting all honest work while maintaining Bitcoin-level security.
The breakthrough comes through the GHOSTDAG protocol, which mathematically solves the ordering problem that emerges when multiple blocks exist simultaneously. Instead of discarding competing blocks, GHOSTDAG creates a coherent linear ordering by identifying the largest k-cluster of well-connected blocks (colored "blue" for honest work) and relegating outliers and potentially malicious blocks to a "red" set that gets ordered after their referencing blue blocks.
This design enables parallel block production where miners don't compete against each other in a zero-sum game. Every honest miner's work contributes to network security, reducing variance and the centralizing pressure that drives miners toward pools. The result is a system that can process 10 blocks per second with confirmation times under 10 seconds, while maintaining the 50% honest majority security assumption that makes Bitcoin trustworthy.
Kaspa's kHeavyHash proof-of-work algorithm is optimized for the high-frequency block production this architecture enables, while the parameter k (currently set based on network propagation delay) ensures that even at high block rates, the system remains secure against sophisticated attacks that try to manipulate the DAG structure.
▨ Key Components & Features
1️⃣ GHOSTDAG Consensus Protocol
The mathematical foundation that enables multiple simultaneous blocks by creating deterministic ordering rules. It inherits the security properties of the heaviest chain while accepting all honest work, eliminating the artificial competition that drives mining centralization.
2️⃣ BlockDAG Architecture
Unlike linear blockchains, this directed acyclic graph allows blocks to reference multiple predecessors, creating a web structure where parallel processing becomes possible. Each block includes all "tips" the miner observed, maximizing inclusion of honest work.
3️⃣ kHeavyHash Mining Algorithm
A memory-hard proof-of-work function optimized for rapid block production and ASIC resistance. The algorithm balances mining decentralization with the performance requirements of 10-blocks-per-second operation.
4️⃣ Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment (DAA)
Real-time difficulty adjustment that responds to hashrate changes within seconds rather than weeks, maintaining consistent 0.1-second average block times regardless of mining participation fluctuations.
5️⃣ Subprotocol Framework
Modular architecture supporting block pruning, SPV proofs, reachability queries, and future programmability through vProgs (virtual programs) without requiring hard forks for basic functionality upgrades.
▨ How Kaspa Works
🔹 Step 1: Parallel Block Creation
Miners observe all current network "tips" (blocks with no children) and create new blocks that reference every tip they've seen, rather than competing to extend a single chain. This happens simultaneously across the network at 10-blocks-per-second intervals.
🔹 Step 2: DAG Formation and Propagation
New blocks are broadcast immediately and form a DAG structure as they reference multiple predecessors. The network topology naturally creates past, future, and anticone sets for each block based on reachability relationships within the graph.
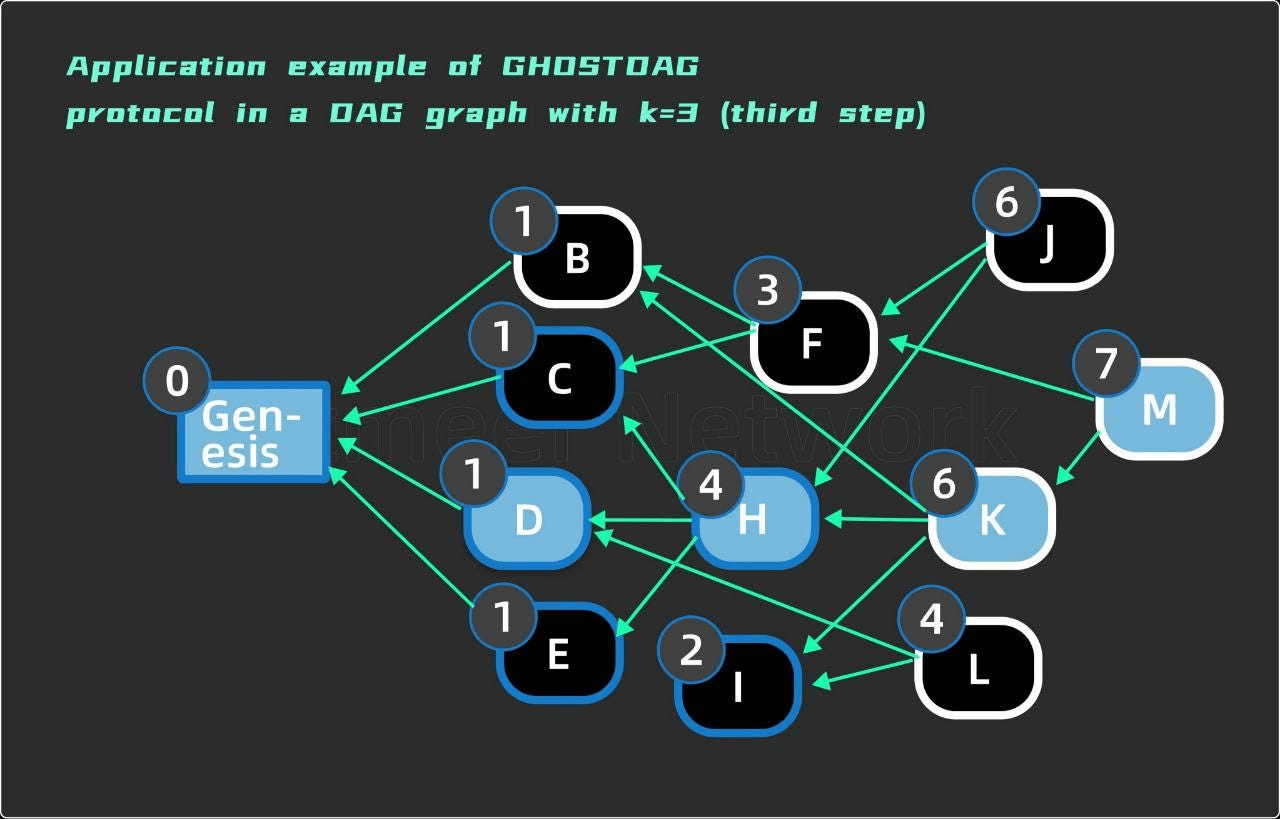
🔹 Step 3: GHOSTDAG Ordering Resolution
The protocol recursively identifies the largest k-cluster of well-connected blocks (blue set) by inheriting from the tip with the highest blue score, then adds anticone blocks that preserve the k-cluster property. Red blocks (potential attacks or poorly connected) are ordered after their referencing blue blocks.
🔹 Step 4: Transaction Processing and Validation
Transactions are ordered according to their containing blocks' positions in the GHOSTDAG ordering, then processed sequentially to prevent double-spends. Only transactions consistent with the current state are accepted, while conflicting ones are rejected.
🔹 Step 5: Confirmation and Finality
Confirmation confidence grows exponentially with time and depth in the DAG, similar to Bitcoin but much faster due to the 10-blocks-per-second rate. Risk of reordering becomes negligible within 10 seconds for typical transactions, achieving practical finality without sacrificing security guarantees.
▨ Token Utility & Flywheel
KAS is the native cryptocurrency of the Kaspa blockchain, launched in November 2021 through a completely fair distribution model with zero premine, no pre-sales, and no team or VC allocations. The token has a maximum supply of 28,704,026,601 KAS, with approximately 26,972,238,251 KAS currently circulating (94% of max supply) as of December 2025.
KAS follows a unique chromatic emission schedule that started at 440 KAS per block and reduces geometrically by (1/2)^(1/12) each month, effectively halving the emission rate annually. This smooth reduction model ensures predictable inflation without the shock effects of traditional Bitcoin-style halvings.
Token Use Cases:
✅ Payments: Who Uses KAS and For What Over 115 businesses globally accept KAS payments directly, spanning categories from retail stores and restaurants to tech services and education providers across Germany, Israel, USA, Romania, Sri Lanka, and Nigeria. Payment infrastructure includes integration with NOWPayments API, CoinPal invoicing, and CryptocurrencyCheckout for e-commerce, while Kasway POS enables decentralized in-person payments with real-time wallet settlements.
The network processed 158 million transactions on October 5, 2025, demonstrating practical capacity for everyday payments, cross-border remittances, and microtransactions that remain economically viable due to fees below $0.001. Community discussions highlight KAS usage for coffee purchases, international transfers, and merchant payments as alternatives to traditional banking systems.
✅ Rewards: How Contributors Earn KAS rewards are distributed exclusively through proof-of-work mining using the kHeavyHash algorithm, maintaining Bitcoin-style incentive alignment without any staking mechanisms. Miners earn both block rewards (currently ~51.91 KAS per second in the chromatic phase) plus transaction fees of 0.0001 KAS per UTXO input.
The fair launch model means 100% of KAS tokens have been earned through competitive mining since mainnet launch, with no founder rewards or investor allocations diluting miner economics. As emissions approach 95% completion by mid-2026, miners will transition to earning primarily through transaction fees, creating sustainable long-term incentives as network usage scales.
✅ Staking: No Economic Skin-in-the-Game Required Kaspa operates as pure proof-of-work without any staking, delegated proof-of-stake, or hybrid consensus mechanisms. This design choice prioritizes permissionless participation and energy-based security over token-weighted governance, meaning network security derives from computational work rather than capital lockup.
The absence of staking eliminates validator centralization risks, slashing conditions, and the complexity of proof-of-stake economic models, maintaining simplicity similar to Bitcoin while achieving significantly higher throughput through the blockDAG architecture.
✅ Access / Governance: Community-Driven Development Kaspa governance operates through decentralized community coordination via Discord voting and crowdfunding for development initiatives, exchange listings, and marketing campaigns. Technical improvements are proposed through Kaspa Improvement Proposals (KIPs) on GitHub, with 15 active proposals including the completed Rust rewrite and ongoing DAGKnight research.
A separate Kaspa DAO (KDAO token) funds ecosystem projects through formal proposal voting, representing the first DAO built on Kaspa infrastructure. Development funding is managed by community treasurers using a 2/4 multisig wallet, ensuring transparency without centralized control by founders or corporations.
▨ Value Accrual & Growth Model
✅ High-Performance Payment Infrastructure → Kaspa serves as the settlement layer for applications requiring fast, secure, and low-cost transactions. With sub-second visibility and 10-second finality, it enables real-time payment systems that current blockchains cannot support effectively.
✅ Mining Decentralization Incentives → Frequent rewards (every 0.1 seconds vs Bitcoin's 600 seconds) dramatically reduce miner variance, making solo mining economically viable again. This creates sustainable incentives for geographic and operator diversification of hashpower.
✅ Network Security Scaling → As more miners join, the BlockDAG accepts all honest work rather than discarding it, creating a positive feedback loop where increased participation directly translates to stronger security without hitting throughput limits.
✅ Programmability and Layer-2 Foundation → The upcoming vProgs framework and ZK-rollup integration (scheduled for 2025-2026) position Kaspa as a high-performance base layer for DeFi and smart contract applications that require Bitcoin-level security with Ethereum-level functionality.
✅ Adoption Flywheel Through Performance → Superior transaction speed and low fees drive user adoption, which increases network value and mining rewards, attracting more hashpower that further strengthens security and decentralization — creating a self-reinforcing cycle that scales with usage rather than hitting capacity walls.
▨ Protocol Flywheel
The Kaspa protocol creates a self-reinforcing growth cycle that strengthens with increased usage. As more applications build on Kaspa's high-performance infrastructure, transaction volume increases, driving up fee revenue and network value. This attracts additional miners who benefit from frequent, low-variance rewards due to the 10-blocks-per-second structure and the inclusion of all honest work.
Growing hashrate increases network security, making Kaspa more attractive for high-value applications and institutional adoption. The parallel block processing means this increased activity doesn't create congestion or fee spikes, instead, it validates the network's capacity to handle real-world scale. As the ecosystem matures toward the planned 32-blocks-per-second and eventually 100-blocks-per-second targets, Kaspa becomes increasingly differentiated from both Bitcoin's limited throughput and proof-of-stake chains' security tradeoffs.
The fair launch model (zero premine, zero VC allocation) ensures that network effects benefit all participants rather than early investors, creating stronger community-driven adoption. Combined with the upcoming programmability features and ZK-rollup integration, this positions Kaspa to capture value from both the digital money use case (Bitcoin's territory) and the smart contract/DeFi ecosystem (Ethereum's territory), without the performance compromises that limit both networks.




