Résumé
A security audit provides a detailed analysis of a project's smart contracts. Conducting an audit is important to ensure the safety of investors' funds. Indeed, all transactions on the blockchain being final, in the event of theft, the funds cannot be recovered. During an audit, auditors examine the smart contract code, produce a report which will then be sent to the team for use. A final report is then published, detailing the errors and the means already put in place to resolve performance or security problems.
Introduction
Audits of smart contracts are very common in the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. If you have invested in a blockchain project, your decision may be based in part on the results of the smart contract audit.
Although most people understand the importance of cybersecurity audits, few delve into the code. Let's take a look at the methods, tools, and results typically observed in smart contract security audits so you can make informed decisions.
What is a smart contract audit?
A smart contract security audit examines and comments on a project's smart contract code. These contracts are generally coded in Solidity and available on GitHub. Security audits are particularly important for DeFi projects, which manage multi-million dollar blockchain transactions across large numbers of users. Audits generally take place in four stages:
1. Smart contracts are provided to auditors for analysis.
2. Auditors present their findings to project managers so that they can act accordingly.
3. The project team makes the necessary changes.
4. The auditors publish a final report taking into account the project team's changes.
For many crypto users, auditing smart contracts is essential before investing in a DeFi project. This is a mandatory step for projects wanting to be taken seriously. Some audit providers are considered leaders in the sector, making their audits certainly more expensive, but more qualitative.
Why do you need to audit your smart contracts?
With large amounts of value locked in or passing through smart contracts, it is understandable that they are attractive targets for cyber attacks. Very small errors in the code can result in the theft of huge sums of money. The DAO hack of the Ethereum blockchain cost nearly $60 million in Ethereum and led to a hard fork of the Ethereum network.
Since blockchain transactions are irreversible, it is essential to ensure that a project's code is completely secure. The highly secure nature of blockchain makes it difficult to recover funds and resolve issues after the fact, so it is best to avoid vulnerabilities at all costs.
How do smart contract audits work?
The process of a smart contract audit is fairly standard among audit providers. Although each auditor's approach may differ slightly, the typical process is as follows:
1. Determine the scope of the audit. The smart contract and project specifications are defined by the project (their objective) and the overall architecture. A specification helps the audit team understand the project's goals when writing and using code.
2. Provide an initial quote based on the amount of work required.
3. Carry out tests. Their exact nature will change depending on the audit team, its analysis tools and its methods. Typically, both manual and automated testing is performed.
4. Create a first version of the report with the errors found to provide it to the project team so that they can give their opinion and make the necessary corrections.
5. Publish the final report, taking into account any actions taken by the team to address the issues raised.
Smart contract audit methods
Gas efficiency
Smart contract audits do not only focus on blockchain security. They also check the code for efficiency and optimization. Some contracts require a complicated series of transactions to perform the function for which they were designed. Since gas fees on networks like Ethereum are relatively expensive, optimized contracts save a lot of money on transaction costs.
Optimization is a good way to judge the competence of a developer. Unnecessary steps increase the risk of problems and should be avoided. When the price of gas is high, smart contracts may not execute, or the gas limit is too low.
Contract vulnerabilities
Most audits involve checking contracts for security vulnerabilities. While some problems are easy to spot, many exploits use advanced techniques and strategies to drain funds. Market manipulation can, for example, be used with vulnerable smart contracts to trigger flash loans. To find these problems, auditors attack the contract in different ways. Some of the most common vulnerabilities include:
1. Reentrancy problems: when a smart contract makes an external call to another external contract before the effects are resolved. The external contract can then recursively call the original smart contract and interact with it in a way normally not possible, as the balance of the original contract has not yet been updated.
2. Integer overflows and underexecutions: when a smart contract performs an arithmetic operation, but the result exceeds the storage capacity (usually 18 decimal places). This often leads to incorrect calculations.
3. Opportunities for anticipation: poorly structured code can help anticipate purchases or sales in the market. Some can take advantage of this information to make positive trades.
Platform security flaws
Most audits include examining the network hosting the contracts and even the API used to interact with the DApp. A project may be vulnerable to a DDoS attack or have its website user interface compromised, allowing hackers to regain access to the wallet of users logging into it.
What is an audit report?
The audit report is provided at the end of the audit process. For the sake of transparency, projects generally share the results with their community. Most reports classify issues by severity: critical, major, minor, etc. The report also lists the status of flaws, with projects given time to fix them before the final report is released.
In addition to a summary, a standard report contains recommendations, examples of redundant codes, and a comprehensive analysis of coding errors. The project is given time to act on the conclusions of the report before publication of the final version.
Where can I have my smart contracts audited?
A number of smart contract auditing services have become famous for their services. Two of them are particularly popular and to obtain an audit from them, you will need to establish an initial quote and submit information.
CertiK
CertiK is an industry leader in smart contract audits. Hundreds of projects trust them. PancakeSwap, the largest Automated Market Maker (AMM) on the BSC, is a good example. Below is part of PancakeSwap's Certik audit.
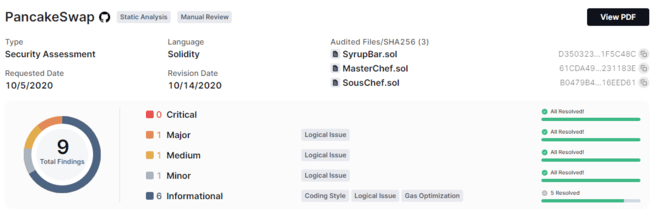
Additionally, the vast majority of projects supported by Binance Labs are audited by CertiK. CertiK publishes a dashboard of audited projects that allows you to compare each of them, as well as a security score. Note that in addition to Ethereum, Ceritk also audits projects based on Polygon and the BSC.

ConsenSys Diligence
Led by Joseph Lubin, one of the co-founders of Ethereum, ConsenSys is one of the biggest names in the cryptocurrency industry when it comes to blockchain development. Under ConsenSys Diligence, the company offers audits of Ethereum smart contracts. They also provide an automated service that checks Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) contracts for the most common errors.
How much does a smart contract audit cost?
The exact cost of an audit depends on the number of smart contracts to be verified. Typically, an audit costs several thousand dollars. A project with many contracts will quickly rise to over $10,000. The audit company handling your audit and its reputation will also impact the amount payable.
To conclude
Fortunately for investors and users, smart contract audits are now a norm. However, since each project now has one, this is no longer a guarantee of quality. This is why it is extremely important that you read the audit yourself. Even if you don't have the technical knowledge to read it, still take a look at the comments.
When you encounter an audit, you will at least be able to understand its contents more easily. As always, make sure that any investment decision takes into account as many elements as possible.


