The blockchain ecosystem has evolved rapidly, with layer‑1 platforms increasingly targeting institutional and regulated financial applications. Dusk Network has emerged as a standout by offering a modular, multi-layer architecture composed of DuskDS (data & settlement), DuskEVM (EVM execution), and DuskVM (privacy execution). Central to this ecosystem is DUSK, the sole native token that fuels all three layers.
This article explores how DUSK’s multi-layer utility—spanning staking, governance, transaction fees, and privacy-preserving application operations—affects liquidity, incentive alignment, and cross-layer value transfers, making it uniquely suited for regulated financial applications.
1. DUSK as the Backbone of a Multi-Layer Architecture
Dusk’s architecture is purpose-built to serve institutional-grade financial applications while maintaining privacy, compliance, and interoperability. Each layer in this stack has a specific function:
1.1 DuskDS (Data & Settlement Layer)
Handles consensus, staking, and transaction settlement.
Stores succinct validity proofs, keeping full nodes lightweight.
Acts as the backbone for cross-layer communication.
1.2 DuskEVM (Execution Layer)
EVM-compatible, enabling deployment of Solidity smart contracts.
Serves as the primary venue for DeFi and regulated applications.
Supports homomorphic encryption and zero-knowledge proofs via Hedger for privacy-compliant operations.
1.3 DuskVM (Privacy Layer)
Dedicated to fully privacy-preserving applications.
Uses the Phoenix output-based transaction model and Piecrust virtual machine.
Provides encrypted computation and confidential asset operations.
Within this structure, DUSK is the only native token. Unlike other ecosystems that rely on multiple tokens for different layers, DUSK is multi-purpose, making it the unifying medium of value, governance, and incentives.
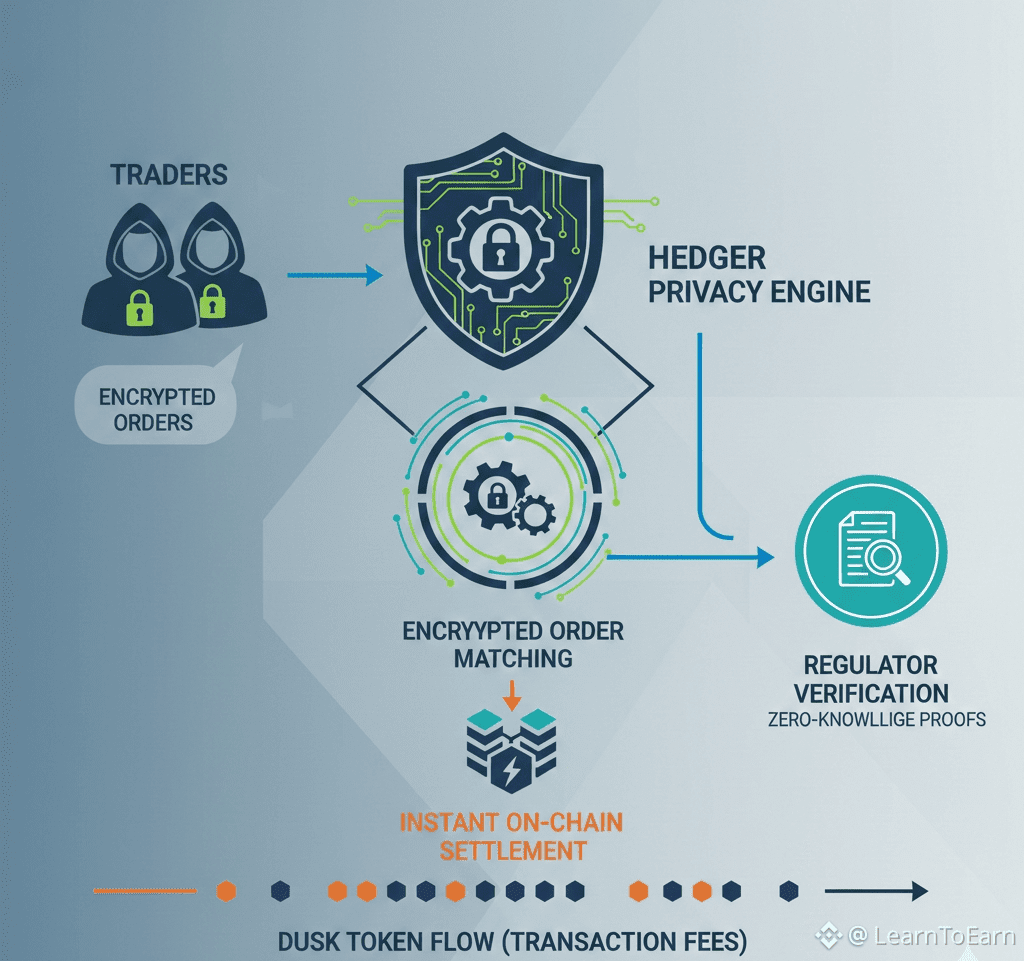
2. Multi-Layer Utility of DUSK
DUSK’s design allows it to serve several essential functions across layers:
2.1 Staking and Security
Validators stake DUSK on DuskDS to secure the network and process transactions.
Staking aligns incentives: validators have skin in the game, which ensures network integrity.
DUSK staked on DuskDS enables cross-layer transaction verification, supporting DuskEVM and DuskVM applications.
Impact: Staking consolidates liquidity on-chain, reduces risk of double-spending, and incentivizes validator participation.
---
2.2 Governance
DUSK holders exercise governance rights across the network.
Governance decisions include:
System upgrades
Transaction fee adjustments
Privacy protocol parameters
Validator reward mechanisms
Multi-layer effect: Governance is unified; a single token controls decisions affecting settlement, execution, and privacy layers. This prevents fragmentation of governance and ensures cohesive policy implementation.
---
2.3 Transaction Fees
DUSK is used as gas for executing smart contracts on DuskEVM.
It also pays for privacy-preserving computation on DuskVM.
Fees collected are redistributed to stakers, creating a feedback loop between network usage and security incentives.
Impact: Gas fees in DUSK encourage efficient use of resources, while simultaneously increasing liquidity demand for the token. Higher adoption of applications naturally drives token velocity.
---
2.4 Privacy-Preserving Application Operations
Hedger-enabled operations, like obfuscated order books, confidential transfers, and encrypted settlements, require DUSK for computation.
DUSK is burned or temporarily locked to validate proofs or secure confidential execution.
Impact: Privacy-focused transactions create intrinsic demand for DUSK, incentivizing both institutional and retail participants to hold and use the token.
---
3. Incentive Alignment Across the Network
A critical innovation of Dusk’s multi-layer token model is aligned incentives across all participants:
3.1 Validators
Earn staking rewards and transaction fees in DUSK.
Incentivized to secure the chain and validate cross-layer transactions.
Penalties for misbehavior (slashing) discourage malicious activity, preserving network trust.
3.2 Developers and Institutions
DUSK is needed to deploy and operate smart contracts and privacy-preserving applications.
Institutions issuing tokenized real-world assets require DUSK to settle trades, manage asset custody, and execute compliance proofs.
This creates a natural alignment between network growth and token utility.
3.3 Users
Pay transaction fees and use DUSK for participation in DeFi or regulated financial applications.
Demand for privacy and compliant execution drives long-term holding and circulation, enhancing network liquidity.
Summary: Every stakeholder—validators, institutions, and end-users—interacts with the same token, creating cohesive economic incentives across layers.
---
4. Cross-Layer Value Transfers
DUSK enables trustless, native bridging between layers:
4.1 From DuskDS to DuskEVM
Staked DUSK can be temporarily unlocked for use in executing smart contracts.
Settlement proofs from DuskDS can directly authorize token transfers on DuskEVM.
Ensures atomic, secure, and verifiable transfers between consensus and execution layers.
4.2 From DuskEVM to DuskVM
Privacy applications require DUSK for encrypted computations.
Users can lock DUSK on DuskEVM and execute confidential operations on DuskVM.
Outputs, such as proof of compliant trades, can then be returned to DuskEVM for public interactions.
4.3 Benefits of Native Cross-Layer Integration
No need for wrapped tokens or custodial bridges.
Reduces operational overhead for institutions.
Improves transaction finality and security.
Supports composable financial instruments where settlement, governance, and privacy coexist seamlessly.
---
5. Liquidity Implications
DUSK’s multi-layer design impacts liquidity in several ways:
5.1 Continuous Demand
Staking, governance, transaction fees, and privacy applications all require DUSK.
Each layer adds independent but complementary demand, stabilizing liquidity.
5.2 Incentivized Circulation
Validators earn DUSK from fees and staking, which re-enters the ecosystem, creating velocity.
Institutions buy DUSK for deploying applications and settlements, further stimulating market depth.
5.3 Exchange Integration
DUSK is increasingly listed on exchanges with cross-chain interoperability.
Its multi-layer utility encourages holding, rather than pure speculation, supporting sustainable liquidity.
---
6. Facilitating Regulated Financial Applications
DUSK’s multi-layer utility is especially impactful in regulated markets:
6.1 Tokenized Securities
DUSK fuels issuance, settlement, and custody operations for tokenized real-world assets.
Validators and institutions can settle trades without revealing sensitive information, while regulators can audit selectively.
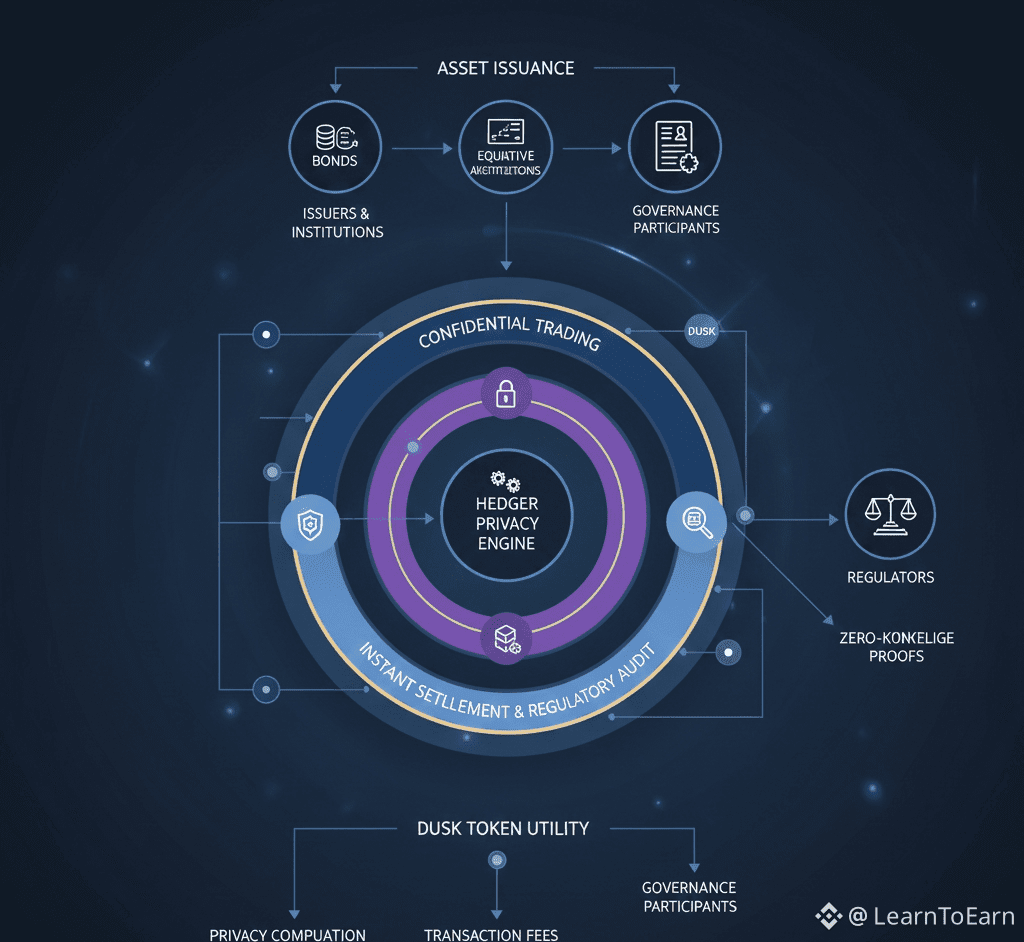
6.2 Composable DeFi
Standard Solidity contracts on DuskEVM can interact with regulated assets, using DUSK as collateral, fees, or governance token.
Enables financial institutions to create hybrid products: tokenized ETFs, structured products, or lending protocols, all compliant and auditable.
6.3 Privacy-Compliant Operations
Hedger ensures that confidential transfers and order matching remain secure.
DUSK serves as the operational currency for private execution, aligning privacy with liquidity incentives.
---
7. Incentive Design and Economic Sustainability
A token with multi-layer utility requires careful economic design:
7.1 Demand-Supply Mechanics
DUSK supply is fixed, creating scarcity.
Multi-layer demand increases effective usage across staking, execution, and privacy operations.
Token velocity is stabilized as each layer creates independent, non-competing demand.
7.2 Reward Redistribution
Fees from transactions and privacy operations are recycled to stakers, ensuring validators and nodes are consistently incentivized.
Institutions benefit from efficient, low-cost operations, encouraging adoption and network activity.
7.3 Governance Alignment
Governance decisions, such as adjusting staking yields or transaction fees, are internally consistent across layers.
This prevents conflicts of interest between layers or user groups.
---
8. Comparative Advantage: Why DUSK’s Multi-Layer Model Matters
Many blockchain ecosystems face fragmentation:
Ethereum: Gas token is separate from staking or governance utility.
Polkadot: DOT primarily secures the relay chain; parachain assets are separate.
Layer 2s: Require bridging, wrapped tokens, or custodial solutions.
DUSK, by contrast, consolidates utility across all layers:
Single token simplifies adoption for institutions.
Native cross-layer bridges reduce risk and friction.
Multi-layer staking and fee design ensures both liquidity and compliance.
Privacy operations are natively integrated, not optional.
This reduces operational complexity and makes Dusk uniquely suitable for regulated financial applications.
---
9. Future Implications
DUSK’s multi-layer model unlocks several long-term possibilities:
9.1 Institutional Adoption
Banks, asset managers, and exchanges can operate entirely within a DUSK-denominated ecosystem, with privacy, compliance, and governance embedded.
9.2 Cross-Layer Composability
Developers can design DeFi protocols, tokenized assets, and privacy applications that interact across layers seamlessly.
9.3 Multi-Asset Liquidity Pools
DUSK can act as a universal settlement token across assets, ensuring liquidity even in complex financial instruments.
9.4 Regulatory Standardization
A single token model simplifies reporting, auditing, and compliance verification, making Dusk a potential benchmark for regulated blockchain infrastructure.
---
10. Challenges and Considerations
While promising, the DUSK token model is not without challenges:
10.1 Adoption Complexity
Institutions must understand cross-layer operations.
Developers need education on Hedger privacy features.
10.2 Scalability and Performance
Multi-layer operations, especially privacy-preserving computations, require optimized nodes and proof generation.
Dusk’s modular design addresses this, but resource-intensive workloads need monitoring.
10.3 Regulatory Dynamics
DUSK enables selective disclosure, but regulations vary across jurisdictions.
Maintaining flexibility without compromising cryptography is key.
---
11. Conclusion
DUSK is more than a native token—it is the unifying economic engine of the Dusk modular ecosystem. Its multi-layer utility:
Secures the network through staking.
Empowers governance decisions.
Enables transaction execution on DuskEVM.
Supports privacy-preserving applications on DuskVM.
By integrating staking, fees, governance, and privacy operations into a single token, DUSK drives:
Aligned incentives across validators, developers, and institutions.
Stable liquidity across regulated and privacy-compliant applications.
Efficient cross-layer value transfers without wrapped assets or custodians.
For tokenized real-world assets, this model is revolutionary. Institutions can issue, trade, and settle assets privately, auditable, and fully compliant, all within a single token-driven ecosystem.
As blockchain adoption expands into regulated finance, DUSK’s multi-layer token design positions Dusk Network to be a leading infrastructure for compliant, privacy-conscious, and highly liquid digital finance.


